Diving Deep into Common Law: Unraveling Its Foundations and Significance
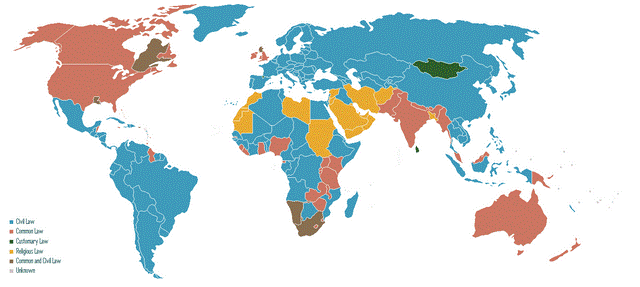
Welcome to the intricate world of Common Law! This legal system, also known as judge-made law or case law, stands in stark contrast to civil law and forms the foundation of legal systems in countries like the United States, Canada, Australia, and the United Kingdom. Buckle up, as we embark on a journey to understand its core principles and historical roots.
The Cornerstones of Common Law:
- Precedence: This is the fundamental principle where judges rely on past court decisions (previous rulings) to decide new cases with similar facts. Each ruling becomes a precedent, creating a body of law that evolves over time.
- Stare Decisis: This Latin term translates to “let the decision stand” and emphasizes the importance of adhering to established precedents to ensure consistency and stability in the legal system.
- Reasoning and Logic: Judges analyze facts, apply legal principles, and justify their decisions through reasoned arguments, creating a transparent and traceable decision-making process.
Origins and Evolution:
The roots of common law can be traced back to 11th-century England, where royal judges developed a standardized set of rules based on local customs and practices. Over centuries, these rulings were documented and became binding precedents, shaping the common law system as we know it today.
Key Features and Distinctions:
- Flexibility: Common law adapts to changing social circumstances through new judicial interpretations, making it relatively dynamic compared to codified legal systems like civil law.
- Judicial Discretion: Judges play a pivotal role in interpreting precedents and creating new ones, leading to potential concerns about inconsistency and subjectivity.
- Adversarial System: Legal proceedings involve opposing parties presenting arguments and evidence, with the judge acting as an impartial observer who ultimately delivers a verdict.
Criticisms and Considerations:
- Accessibility and Complexity: The reliance on past rulings can make the law complex and challenging to navigate, especially for individuals without legal expertise.
- Equity Considerations: In certain situations, strict adherence to precedent might hinder achieving fair and just outcomes, prompting the creation of equitable remedies.
- Global Landscape: While common law holds significant influence, understanding its nuances is crucial when exploring different legal systems across the world.
Exploring Further:
This deep dive merely scratches the surface of the vast and fascinating world of common law. To delve deeper:
- Read landmark common law cases and analyze the reasoning behind the decisions.
- Research the historical development of common law in different countries.
- Explore the interplay between common law and other legal systems like civil law.
- Consider the ongoing debates about the strengths and weaknesses of common law in the modern world.
Remember, legal systems are dynamic and multifaceted. Understanding the foundations of common law equips you to engage in informed discussions and critically evaluate its role in shaping our world.